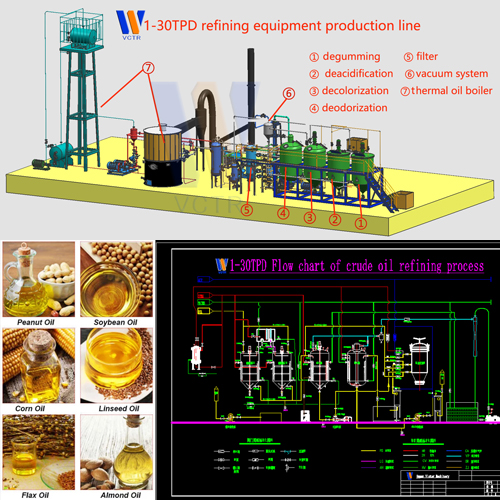
Decolorization of oil refining

The purpose of decolorization is to reduce the color in the oil, remove harmful substances, and increase the shelf life of the oil
So what are the factors that affect decolorization, and what is the scientific method of decolorization?
1. Decolorant
(1) Activated bleaching earth:It has strong adsorption capacity for chlorophyll and colloidal impurities, such as protein, phospholipid, mucus, and has stronger adsorption for basic red and polar atoms, and weak adsorption for small molecule pigments. For storage pigments and processed pigments, the decolorization rate is low, such as degumming oil stored for more than 2 years and soybean oil stored for more than 5 years, the decolorization effect is poor. Activated clay has a strong oil absorption of 30%-50%. The amount of residual oil depends on the operation of the filter and the performance of the activated clay. For fats that are easy to oxidize and polymerize, the amount of residual oil is relatively high. In addition, activated clay has high activity, which is easy to hydrolyze oil and increase the acid value of decolorized oil. Generally, adding 1% activated clay will increase the acid value (KOH) of decolorized oil by 0.01 mg/g, which will cause the hydrolysis and oxidation of oil and the color of oil. Catalyzes oil oxidation and isomerization.
(2) Activated carbon: It absorbs high molecular substances with complex structure, absorbs red and green pigments in oil, and absorbs macromolecular polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and residual pesticides. It has a high oil absorption rate and slow filtration after decolorization.
(3) Attapulgite: Absorb small molecule pigments, refined oil has good oxidation stability, short decolorization time, low oil absorption, poor filtration performance, and relatively large particle size is required. A two-step decolorization technique is adopted with a low-activity decolorizing agent. The adsorption capacity of attapulgite: adsorption of saponin> adsorption of pigment> adsorption of phospholipids.
(4) Diatomaceous earth: mostly used as filter aid. The decolorization rate of attapulgite and diatomite is less than 50% of activated clay.

2. Decolorization operation
The quality requirements of the oil to be decolorized: the residual phosphorus content is less than or equal to 5 mg/kg, the moisture content is less than 0.5%, and the residual soap content is 50 mg/kg. The particle size of the clay is controlled to be greater than or equal to 90% through a 200-mesh sieve, and the less than 10 μm, the better.
Adding activated clay before oil heating, 75~85℃ can inhibit the heating oil from deepening, and prevent pigment oxidation reduction and the affinity of activated clay. The main issues to pay attention to when decolorizing:
(1) Temperature: When operating under vacuum, activated clay decolorizes at 75-85°C; de-yellows at 50-130°C; Carotene is unstable to heat, and decolorizes at 150-170°C. Note that prolonging the decolorization time at high temperature will cause the grease to recolor.
At low temperatures, the viscosity of the oil becomes larger, and the activated clay is weaker in adsorbing pigments. High temperature will solidify pigments, produce new pigments, polymerization and isomerization, and accelerate desorption, decrease the decolorization rate, and increase fuel consumption. At high temperatures, the prolongation of the contact time between grease and adsorbent may produce fatty acid double bond conjugation, resulting in 0.1% to 0.2% Conjugated fatty acids, bring peculiar smell. In addition, at high temperatures, the water in the activated clay will evaporate, which will disintegrate the bentonite or montmorillonite crystal lattice and lose part of the active surface.
As the decolorization temperature increases, the acid value of the oil increases. The temperature has a critical point for the acid value of the decolorized oil. If the temperature exceeds the critical point, the FFA will increase greatly. At 100-105°C, 30 min, 120°C, 5 min, the color of the fat and oil rises, the acid value rises, the fat is oxidized, and it smells of clay. Too high decolorization temperature and too long time will cause the oil to turn back to acid.
For the decolorization of soybean oil, the temperature should be 105~112℃, and for the stock oil, the temperature should be 100~110℃.
(2) Time: After the adsorbent is saturated for 25 minutes, and the time is extended, the oxidation rate of the oil will increase. If the adsorption speed is exceeded, the oil color will rise and the acid value will rise.
(3) Stirring: The design of the length, speed and number of the stirring blades during adsorption and decolorization should ensure that the grease and the adsorbent establish a dynamic and uniform contact and adsorption balance, and avoid long local contact time or local static. Under negative pressure, it is mixed vigorously, but it should not cause grease splash.
The mixing of the white clay pre-mixing tank is the key. The steam jet is linear, and there are dead corners, which cannot form turbulence; the length of the mechanical mixing blade must be long enough to form turbulence on the surrounding inner walls. Mechanical mixing should be equipped with high-quality mechanical seals, and the mixing intensity should be high to avoid heterogeneous mixing.
(4) Addition ratio: As the amount of activated clay increases, the concentration of activated clay in the oil reaches saturation, the adsorbent particles affect each other, and the change in decolorization rate becomes smaller. For refining Brazilian soybean oil, the ratio of activated clay to attapulgite is 1:2 or the ratio of activated clay, filter aid and attapulgite is 1:1:2. Attapulgite for refining American soybean oil. Brazilian soybean oil with a heat loss rate of 15%, the ratio of activated clay to attapulgite is 1:1. Refined National Oil Storage (5 years), the ratio of activated white clay to attapulgite is 4:1 or 5:1, Refined National Oil Storage (2 years), the ratio of activated white clay to attapulgite is 2:1, determined according to the sample test Add 0.1%~0.5% activated carbon. The ratio of adsorbent addition is considered from cost, color and acid reversion. The choice of decolorizing agent depends on cost, activity, oil residue and waste clay disposal.
(5) Decolorization process
Adopt the re-decolorization process: first pass the oil to be decolorized through a decolorization filter (the network is covered with filtered oily clay), and perform pre-decolorization while removing residual soaps, phospholipids and other mucilages. Generally, the decolorizing agent can be reduced by 2 to 3 kg/t (Calculated by activated clay). Two-stage counter-current decolorization: compared to adding activated clay at a time, it can save 15%-40% of the amount. Decolorization by filter press: The effective concentration of adsorbent is high, which is close to countercurrent decolorization.

3. Adjust the decolorization equipment
The volume of the decolorization tank is large and the stirring strength is not enough. Consider making a pre-mixing tank with a long and narrow compartment structure combined with mechanical stirring and steam stirring. Grease baffles and overflows in the decolorization tank, and implements "first in, first out". Add decolorizing agent according to the decolorization requirements, control the temperature at 80~95℃ for 5~10 min, enter the decolorization tank and stay for 10~20 min before filtering. The decolorization tank body is provided with an oil distribution pan, which is arranged close to the oil inlet, and a number of deflectors are arranged along the axial direction, and are arranged obliquely downwards. The deflectors are staggered along the axial direction, and the outlet of the upper deflector is located on the lower deflector. Above, the inclination angle of the deflector is 5°~10°. It is advisable to design the inlet pipe of the oil distribution pan with a length of 5-10 cm. The oil distribution pipe has one inlet and 2 to 4 branch pipe outlets to avoid oil piling and splashing. The oil is guided by several layered deflectors. To extend the time. Three layers of decolorization tanks are selected, with a cone bottom at the bottom to avoid oil deposits and short circuits at the bottom and the oil outlet pipeline. Set up the decolorized oil temporary storage tank, its volume can ensure that the filter will not produce overflow tank and undecolorized oil directly enters the decolorization tank when the filter is switched, keep the filter speed of the decolorized oil into the filter stable, and reduce the oil flow rate when the filter is switched. fluctuation.