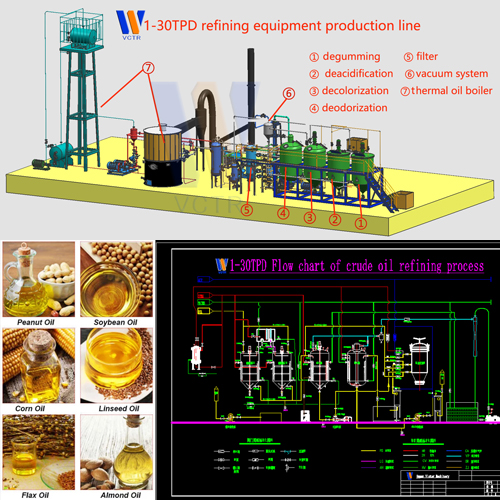
The difference between physical refining and chemical refining of edible oil
The refining methods of edible oil are generally divided into physical refining and chemical refining. The fundamental purpose of these two methods is to remove free fatty acids in oils. In fact, how to remove free fatty acids in edible oils is based on physical refining and chemical refining. The main difference between the chemical refining of edible oils. In the physical refining process of edible oils, free fatty acids are removed by high-temperature steam distillation, while in the chemical refining process of edible oils, free fatty acids are removed by lye neutralization. The principle and detailed operation process of edible oil physical refining and chemical refining will also be somewhat different. The choice of refining method also depends on the type and quality of the oil.
What is physical refining?
The principle of physical refining is to take advantage of the fact that the boiling point of free fatty acids is lower than that of triglycerides to remove FFA in the oil. FFA is the abbreviation for free fatty acids. The physical refining method is a distillation and deacidification process. This method does not require the addition of lye. It relies on vacuum steam distillation to allow the steam to take away the free fatty acids and remove some peculiar smells and substances that are not easy to saponify. Physical refining will not produce soapstock, and the output is relatively high, it is relatively easy to operate, and the water and energy consumption are relatively low. But its disadvantage is that it requires high quality crude oil, which is not suitable for cottonseed oil refining, and that this refining method will produce polymers and trans acids at high temperatures.
1) Degumming: Add phosphoric acid solution to edible oil to obtain colloidal precipitate, and then filter the precipitate.
2) Bleaching: Add activated bleaching earth to the edible oil to absorb the pigment and some other impurities in the oil.
3) Deacidification and deodorization: high-temperature water vapor is passed into the edible oil, free fatty acids are removed by distillation, and the difference in volatility between oil and odor substances is used to remove odor substances in the oil.
What is chemical refining?
Chemical refining is a very old refining method. The main method is to add lye to saponify the free fatty acids in the oil to produce soapstock, and then remove them by centrifugal removal. For small production, we can choose the settling separation method, for large production we have to use a centrifuge for separation. By adding lye, the neutralized oil with FFA must be bleached and deodorized by refining equipment to obtain edible oil. Compared with physical refining, this oil refining method can refine a wider range of oils. In addition to the removal of free fatty acids, this oil refining method can also remove the following substances:
Phospholipids (colloidal impurities), oxides, metal ions (such as iron, copper), pigments (such as gossypol), insoluble impurities (such as meal chips), etc.
1) Degumming: Heating water into edible oil to agglomerate peptic impurities into agglomerates, which are separated after sedimentation.
2) Deacidification: Add lye to edible oil to neutralize free fatty acids, thereby removing free fatty acids.
3) Bleaching: Add activated bleaching earth to the edible oil to absorb the pigment and some other impurities in the oil.
4) Deodorization: pass high-temperature water vapor into the edible oil, and use the difference in volatility between oil and odor substances to remove odor substances in the oil.
What is physical refining?
The principle of physical refining is to take advantage of the fact that the boiling point of free fatty acids is lower than that of triglycerides to remove FFA in the oil. FFA is the abbreviation for free fatty acids. The physical refining method is a distillation and deacidification process. This method does not require the addition of lye. It relies on vacuum steam distillation to allow the steam to take away the free fatty acids and remove some peculiar smells and substances that are not easy to saponify. Physical refining will not produce soapstock, and the output is relatively high, it is relatively easy to operate, and the water and energy consumption are relatively low. But its disadvantage is that it requires high quality crude oil, which is not suitable for cottonseed oil refining, and that this refining method will produce polymers and trans acids at high temperatures.
1) Degumming: Add phosphoric acid solution to edible oil to obtain colloidal precipitate, and then filter the precipitate.
2) Bleaching: Add activated bleaching earth to the edible oil to absorb the pigment and some other impurities in the oil.
3) Deacidification and deodorization: high-temperature water vapor is passed into the edible oil, free fatty acids are removed by distillation, and the difference in volatility between oil and odor substances is used to remove odor substances in the oil.
What is chemical refining?
Chemical refining is a very old refining method. The main method is to add lye to saponify the free fatty acids in the oil to produce soapstock, and then remove them by centrifugal removal. For small production, we can choose the settling separation method, for large production we have to use a centrifuge for separation. By adding lye, the neutralized oil with FFA must be bleached and deodorized by refining equipment to obtain edible oil. Compared with physical refining, this oil refining method can refine a wider range of oils. In addition to the removal of free fatty acids, this oil refining method can also remove the following substances:
Phospholipids (colloidal impurities), oxides, metal ions (such as iron, copper), pigments (such as gossypol), insoluble impurities (such as meal chips), etc.
1) Degumming: Heating water into edible oil to agglomerate peptic impurities into agglomerates, which are separated after sedimentation.
2) Deacidification: Add lye to edible oil to neutralize free fatty acids, thereby removing free fatty acids.
3) Bleaching: Add activated bleaching earth to the edible oil to absorb the pigment and some other impurities in the oil.
4) Deodorization: pass high-temperature water vapor into the edible oil, and use the difference in volatility between oil and odor substances to remove odor substances in the oil.
If you want to know more about information: edible oil physical refining, edible oil chemical refining, edible oil refining, or edible oil refining equipment,You can contact Henan Victor Machinery at any time, and we will provide the most suitable suggestions and solutions according to your requirements.