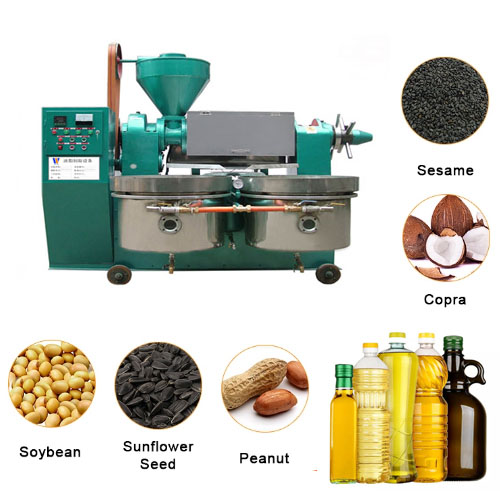
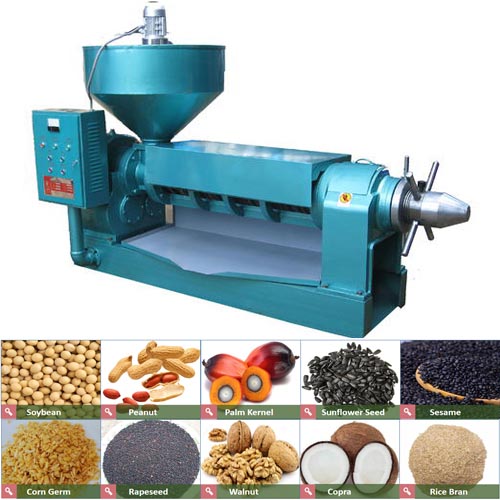
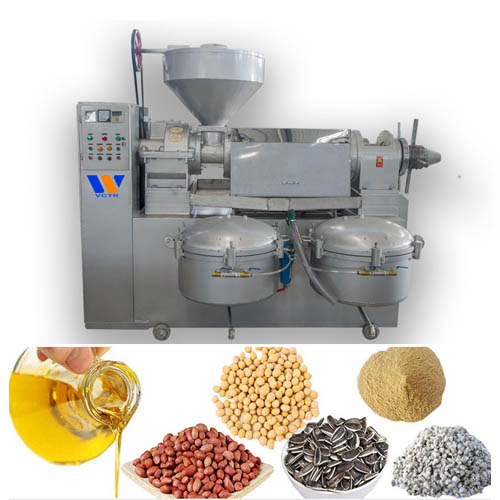
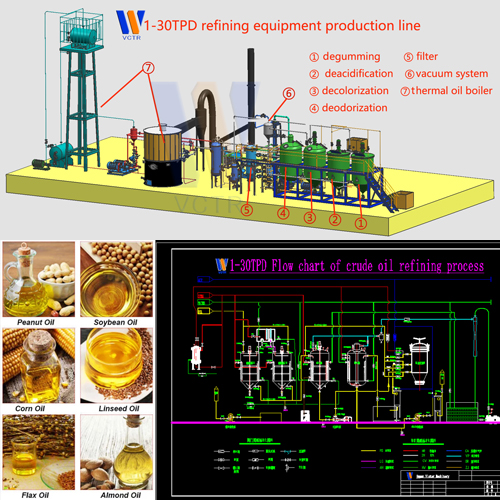
Coconut oil processing technology
Coconut oil processing technology
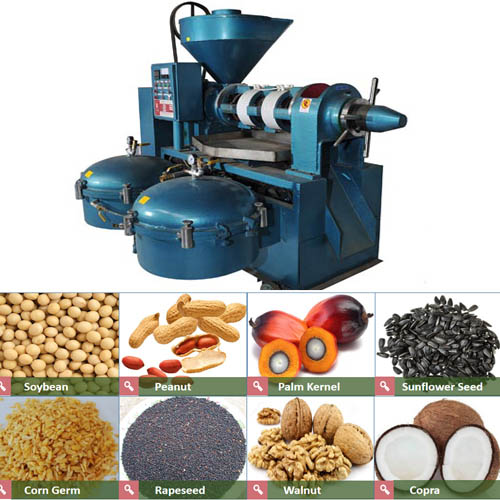
During coconut oil processing,the efficient operation of the screw oil press requires steaming and tempering to control the temperature of the coconut embryo between 91-93℃. Under the condition that the moisture of the coconut embryo is below 91℃ and the moisture is above 4%, the coconut oil output is low, but at 93℃ Above, under the condition that the water content is less than 3%, the dark oil and coke cake from the coconut embryo will produce a lower oil yield. The sieved and precipitated fine particles should not exceed 10% of the fresh raw materials to avoid the formation of fine particles during the steaming and tempering stage and then the pressing process.
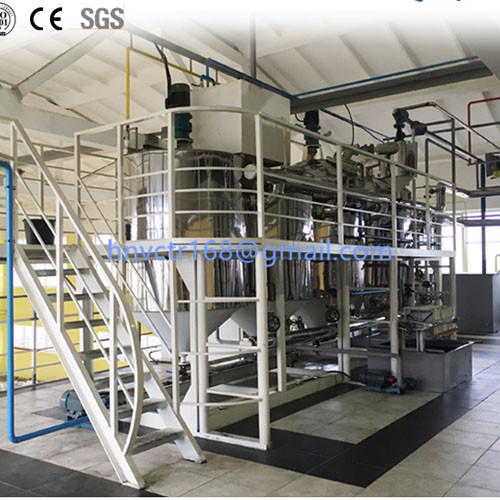
Coconut oil processing technology-Post-pressing process: the oil from the screw press is sent to the wire screen and the clarifying tank, and the particles are separated. The latter will be mixed with the raw materials and enter the system for processing. Each ton of super clear oil must be mixed with 10kg of bleaching earth. After passing through the safety filter, the clean oil is obtained. After storage or further processing, the coconut oil glutinous rice cake is pelletized, bagged and sent to the animal feed factory.
Coconut oil processing technology-Wet processing: In the wet processing, fresh coconut meat is used as the raw material. In addition to the product oil, other edible by-products obtained from coconut oil are: coconut powder, protein, carbohydrates and vitamins. In order to make this process more widely commercialized, the following advantages should be emphasized to obtain high-quality oil And the recovery obtains nutritious (ingredient) by-products, and the latter is lost in the dried coconut.
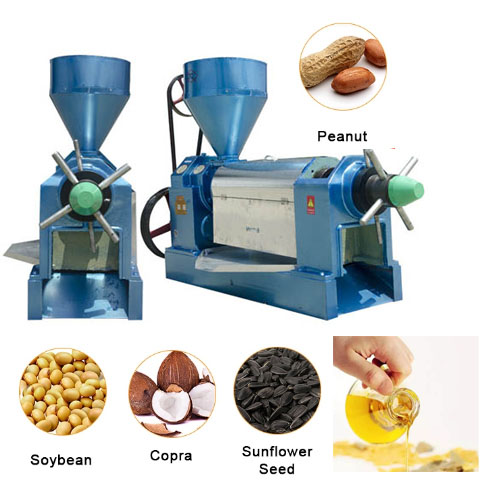
The mature coconut is shelled and separated to obtain the coconut meat, and then peeled to remove the testa. The ectocarp is extracted from the skin oil as a byproduct. The shredded coconut meat is crushed by wedges, a tooth plate crusher and a drum crusher. The crushed powder is squeezed out of coconut juice through a screw press. Coconut juice is filtered through a mesh conveyor, and then centrifuged to separate the oil layer. A small amount of water in the oil is reduced to 0.1%-0.2% by air heating. Generally speaking, 6.8t "natural" coconut oil can be extracted from 25t fresh coconut meat, de-oiled milk is spray-dried to recover protein and carbohydrates. The testa residues obtained by the screw press are ground together into powder to recover oil and make coconut powder.
Coconut oil processing technology-Solvent extraction: The unit operation of solvent extraction is used as a supplement to the mechanical pressing method, which can finally minimize the residual oil in the coconut oil. After the coconut cake undergoes rapid initial extraction, the residual oil content is controlled within 14%-18%; Production almost doubled. N-hexane (boiling point 68.7°C) is widely used as the extraction solvent. In the countercurrent extraction unit, the meal is first contacted with the mixed oil (n-hexane and ten oils), and is washed with pure n-hexane when leaving the extractor. The oil is approximately 3.5%. Recover the n-hexane in the mixed oil and inn, and reuse it for subsequent operations. The overflowing n-hexane vapor is captured by the cold mineral oil spray to avoid danger and increase the recovery rate of the solvent.
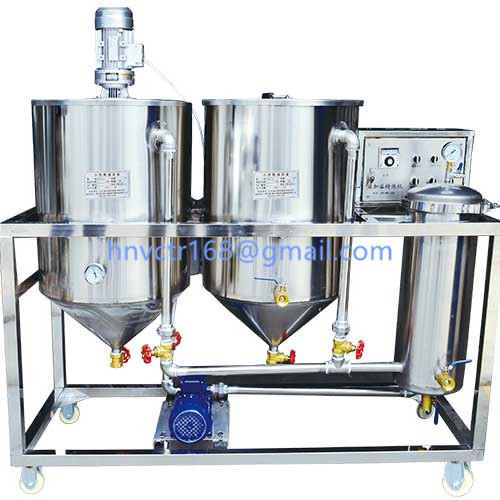
Coconut oil processing technology-Refining: The refining of crude oil includes a series of steps to remove impurities in glycerolipids. Make products edible and extend shelf life. Impurities include fatty acids, phospholipids, metal ions, pigments, oxides, solid particles and unpleasant volatile gases. Crude coconut oil can be refined by any of the following methods: ①Chemical refining (batch oil refinery or continuous) ②Physical refining.
The free fatty acids (FFA) in natural coconut oil are neutralized with a dilute sodium hydroxide solution to obtain a saponified product.
RCOOH+[NA+OH-]→[RCOO-NA+]+H2O
Saponifiable matter together with other impurities in the water phase is called soapstock. In the batch refining process, the soapstock are absorbed and lost by gravity. On the other hand, continuous refining has the following main advantages over batch refining: ①The saponification degree of neutral oil can be reduced to a minimum due to the extremely short contact time between oil and sodium hydroxide (30s-45s). ②Through the action of the centrifuge, the time to separate soapstock and waste water from the oil is significantly reduced.
After alkali refining, it is followed by decolorization. The pigment in the oil is adsorbed by the surface of the bleaching earth and activated carbon particles.
For some oils, the presence of a small amount of water when mixed may improve the efficiency of decolorization. Deodorization is the last step of chemical refining. Volatile odor substances (including low molecular weight fatty acids) are removed by steam stripping under negative pressure.The final product is called RBD coconut oil.
During coconut oil processing,the efficient operation of the screw oil press requires steaming and tempering to control the temperature of the coconut embryo between 91-93℃. Under the condition that the moisture of the coconut embryo is below 91℃ and the moisture is above 4%, the coconut oil output is low, but at 93℃ Above, under the condition that the water content is less than 3%, the dark oil and coke cake from the coconut embryo will produce a lower oil yield. The sieved and precipitated fine particles should not exceed 10% of the fresh raw materials to avoid the formation of fine particles during the steaming and tempering stage and then the pressing process.
Coconut oil processing technology-Post-pressing process: the oil from the screw press is sent to the wire screen and the clarifying tank, and the particles are separated. The latter will be mixed with the raw materials and enter the system for processing. Each ton of super clear oil must be mixed with 10kg of bleaching earth. After passing through the safety filter, the clean oil is obtained. After storage or further processing, the coconut oil glutinous rice cake is pelletized, bagged and sent to the animal feed factory.
Coconut oil processing technology-Wet processing: In the wet processing, fresh coconut meat is used as the raw material. In addition to the product oil, other edible by-products obtained from coconut oil are: coconut powder, protein, carbohydrates and vitamins. In order to make this process more widely commercialized, the following advantages should be emphasized to obtain high-quality oil And the recovery obtains nutritious (ingredient) by-products, and the latter is lost in the dried coconut.
The mature coconut is shelled and separated to obtain the coconut meat, and then peeled to remove the testa. The ectocarp is extracted from the skin oil as a byproduct. The shredded coconut meat is crushed by wedges, a tooth plate crusher and a drum crusher. The crushed powder is squeezed out of coconut juice through a screw press. Coconut juice is filtered through a mesh conveyor, and then centrifuged to separate the oil layer. A small amount of water in the oil is reduced to 0.1%-0.2% by air heating. Generally speaking, 6.8t "natural" coconut oil can be extracted from 25t fresh coconut meat, de-oiled milk is spray-dried to recover protein and carbohydrates. The testa residues obtained by the screw press are ground together into powder to recover oil and make coconut powder.
Coconut oil processing technology-Solvent extraction: The unit operation of solvent extraction is used as a supplement to the mechanical pressing method, which can finally minimize the residual oil in the coconut oil. After the coconut cake undergoes rapid initial extraction, the residual oil content is controlled within 14%-18%; Production almost doubled. N-hexane (boiling point 68.7°C) is widely used as the extraction solvent. In the countercurrent extraction unit, the meal is first contacted with the mixed oil (n-hexane and ten oils), and is washed with pure n-hexane when leaving the extractor. The oil is approximately 3.5%. Recover the n-hexane in the mixed oil and inn, and reuse it for subsequent operations. The overflowing n-hexane vapor is captured by the cold mineral oil spray to avoid danger and increase the recovery rate of the solvent.
Coconut oil processing technology-Refining: The refining of crude oil includes a series of steps to remove impurities in glycerolipids. Make products edible and extend shelf life. Impurities include fatty acids, phospholipids, metal ions, pigments, oxides, solid particles and unpleasant volatile gases. Crude coconut oil can be refined by any of the following methods: ①Chemical refining (batch oil refinery or continuous) ②Physical refining.
The free fatty acids (FFA) in natural coconut oil are neutralized with a dilute sodium hydroxide solution to obtain a saponified product.
RCOOH+[NA+OH-]→[RCOO-NA+]+H2O
Saponifiable matter together with other impurities in the water phase is called soapstock. In the batch refining process, the soapstock are absorbed and lost by gravity. On the other hand, continuous refining has the following main advantages over batch refining: ①The saponification degree of neutral oil can be reduced to a minimum due to the extremely short contact time between oil and sodium hydroxide (30s-45s). ②Through the action of the centrifuge, the time to separate soapstock and waste water from the oil is significantly reduced.
After alkali refining, it is followed by decolorization. The pigment in the oil is adsorbed by the surface of the bleaching earth and activated carbon particles.
For some oils, the presence of a small amount of water when mixed may improve the efficiency of decolorization. Deodorization is the last step of chemical refining. Volatile odor substances (including low molecular weight fatty acids) are removed by steam stripping under negative pressure.The final product is called RBD coconut oil.