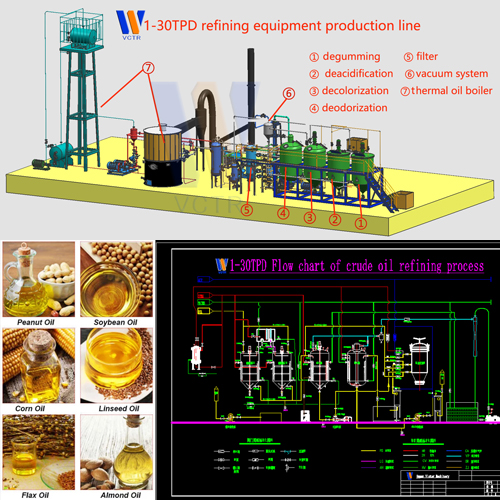
Ventilation and dust removal of control dust in grain factory warehouse(Part 1)
Ventilation and dust removal of control dust in grain factory warehouse
Grain factory warehouses often produce dust during the production process. The use of ventilation methods for air purification (dust removal) and cooling materials in grain processing plants is an essential and important measure. The further transformation of ventilation operation, the use of aerodynamic characteristics, can also carry out air separation and classification of grains, and then develop into a way of conveying powder and granules, namely pneumatic conveying. In addition, reasonable ventilation and dust removal devices play a positive role in preventing the breeding of microorganisms and pests and dust explosion accidents.
In grain enterprises, the most effective way to prevent dust from spreading indoors is to collect them directly in the place where dust is produced, and discharge it outdoors after being purified by a dust collector. This method of ventilation is called local exhaust (suction).
Some enterprises cannot use partial exhaust due to the restriction of production conditions, or after adopting partial exhaust, the concentration of indoor harmful substances still exceeds the sanitary standard. In this case, full ventilation can be adopted. Comprehensive ventilation is to ventilate the workshop and use fresh air to dilute the concentration of harmful substances in the workshop below the maximum allowable concentration. The air volume required for comprehensive ventilation greatly exceeds the local exhaust, and the corresponding equipment is also relatively large.
According to the different working power, the ventilation system can be divided into mechanical ventilation and natural ventilation. Natural ventilation relies on the wind pressure caused by outdoor wind and the thermal pressure caused by the temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air to make air flow. Therefore, natural ventilation does not require special power, and it is an economical and effective ventilation method in some workshops with waste heat. Mechanical ventilation relies on the pressure caused by the ventilator to make air flow.
In some grain enterprises located in the frigid zone, because the outdoor temperature is very low, the air entering the machinery and equipment is taken indoors, but it needs to be processed (including washing and heating). Air is circulated in this way to form a closed loop called a closed recirculation ventilation system. In order to overcome the shortcomings of poor hygienic effects in the closed recirculation ventilation system, some outdoor fresh air (not less than 10%) can be appropriately supplemented (which also needs to be heated to enter the mechanical equipment). This system is called a semi-closed recirculation ventilation system.
For some mechanical equipment with ventilators (such as vibrating screens), in order to achieve "one wind with multiple uses", some areas have been converted into a single air closed circulation system. This saves part of the air duct and dust removal equipment, and is also conducive to energy saving.
The mechanical local exhaust device (or ventilation and dust removal device, ventilation and dust removal network) in the grain enterprise is composed of four parts: ventilator, suction hood, air duct and dust collector.When the ventilator is working, due to the effect of negative pressure, the outside air enters the working area through the gaps in the casing of the machine and equipment and the special air duct, and takes away the dust and heat and water vapor diffused by the machine and equipment when it is working. The air pipe is sent to the dust collector for purification, and then the purified air is discharged outside.
1. Suction hood
The suction hood is a hood that collects dusty air, and it should be installed near the dust source. One end is connected with machinery and equipment, and the other end is connected with a wind pipe. Due to the difference in the structure and operation of the machinery and equipment, the form of the suction hood is varied.
2. Air duct
The duct is a duct that conveys dusty air, and its section is generally circular. The figure below shows the connection form of the suction hood and the branch duct.
3. Dust collector
Dust-laden air must be purified by a dust collector before it can be discharged into the atmosphere. In grain enterprises, the commonly used dust collectors and bag filters can be used alone or in two stages at the same time.
4. Ventilator
The air source of the ventilation network is generally a medium and low pressure centrifugal fan.According to the process flow and the configuration of machinery and equipment, plant conditions and air volume, it can be designed as a separate ventilation and dust removal network (a single machine uses a ventilator suction) or a centralized ventilation and dust removal network(Two or more machines and equipment share a ventilator for suction).
Grain factory warehouses often produce dust during the production process. The use of ventilation methods for air purification (dust removal) and cooling materials in grain processing plants is an essential and important measure. The further transformation of ventilation operation, the use of aerodynamic characteristics, can also carry out air separation and classification of grains, and then develop into a way of conveying powder and granules, namely pneumatic conveying. In addition, reasonable ventilation and dust removal devices play a positive role in preventing the breeding of microorganisms and pests and dust explosion accidents.
In grain enterprises, the most effective way to prevent dust from spreading indoors is to collect them directly in the place where dust is produced, and discharge it outdoors after being purified by a dust collector. This method of ventilation is called local exhaust (suction).
Some enterprises cannot use partial exhaust due to the restriction of production conditions, or after adopting partial exhaust, the concentration of indoor harmful substances still exceeds the sanitary standard. In this case, full ventilation can be adopted. Comprehensive ventilation is to ventilate the workshop and use fresh air to dilute the concentration of harmful substances in the workshop below the maximum allowable concentration. The air volume required for comprehensive ventilation greatly exceeds the local exhaust, and the corresponding equipment is also relatively large.
According to the different working power, the ventilation system can be divided into mechanical ventilation and natural ventilation. Natural ventilation relies on the wind pressure caused by outdoor wind and the thermal pressure caused by the temperature difference between indoor and outdoor air to make air flow. Therefore, natural ventilation does not require special power, and it is an economical and effective ventilation method in some workshops with waste heat. Mechanical ventilation relies on the pressure caused by the ventilator to make air flow.
In some grain enterprises located in the frigid zone, because the outdoor temperature is very low, the air entering the machinery and equipment is taken indoors, but it needs to be processed (including washing and heating). Air is circulated in this way to form a closed loop called a closed recirculation ventilation system. In order to overcome the shortcomings of poor hygienic effects in the closed recirculation ventilation system, some outdoor fresh air (not less than 10%) can be appropriately supplemented (which also needs to be heated to enter the mechanical equipment). This system is called a semi-closed recirculation ventilation system.
For some mechanical equipment with ventilators (such as vibrating screens), in order to achieve "one wind with multiple uses", some areas have been converted into a single air closed circulation system. This saves part of the air duct and dust removal equipment, and is also conducive to energy saving.
The mechanical local exhaust device (or ventilation and dust removal device, ventilation and dust removal network) in the grain enterprise is composed of four parts: ventilator, suction hood, air duct and dust collector.When the ventilator is working, due to the effect of negative pressure, the outside air enters the working area through the gaps in the casing of the machine and equipment and the special air duct, and takes away the dust and heat and water vapor diffused by the machine and equipment when it is working. The air pipe is sent to the dust collector for purification, and then the purified air is discharged outside.
1. Suction hood
The suction hood is a hood that collects dusty air, and it should be installed near the dust source. One end is connected with machinery and equipment, and the other end is connected with a wind pipe. Due to the difference in the structure and operation of the machinery and equipment, the form of the suction hood is varied.
2. Air duct
The duct is a duct that conveys dusty air, and its section is generally circular. The figure below shows the connection form of the suction hood and the branch duct.
3. Dust collector
Dust-laden air must be purified by a dust collector before it can be discharged into the atmosphere. In grain enterprises, the commonly used dust collectors and bag filters can be used alone or in two stages at the same time.
4. Ventilator
The air source of the ventilation network is generally a medium and low pressure centrifugal fan.According to the process flow and the configuration of machinery and equipment, plant conditions and air volume, it can be designed as a separate ventilation and dust removal network (a single machine uses a ventilator suction) or a centralized ventilation and dust removal network(Two or more machines and equipment share a ventilator for suction).