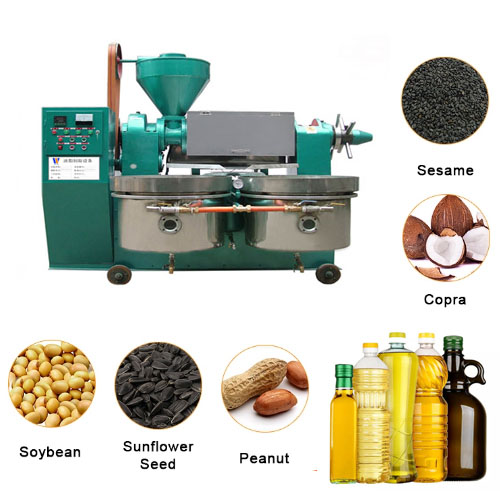
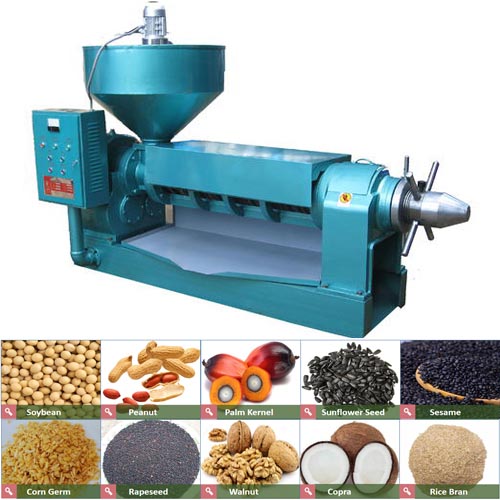
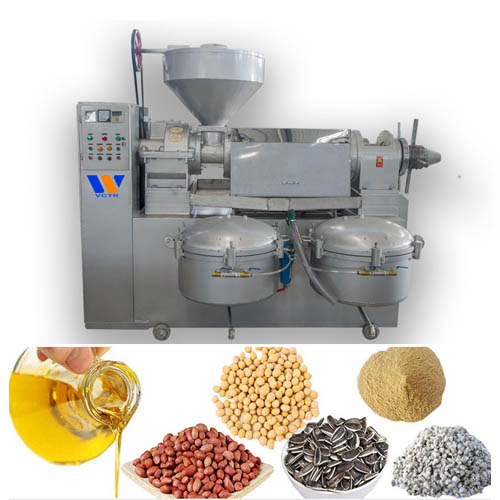
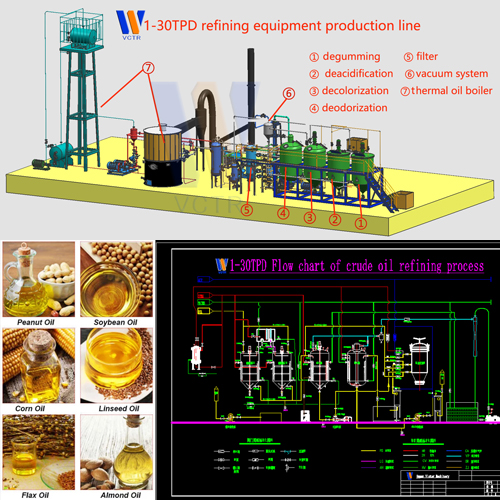
Oil processing products-Hydrogenated oil
1. The basic principle of oil hydrogenation
When heating vegetable oils containing a lot of unsaturated fatty acids, add metal catalysts (nickel series, copper-chromium series, etc.) to pass hydrogen gas, so that the double bonds in the unsaturated fatty acid molecules combine with hydrogen atoms to become fatty acids with a lower degree of unsaturation. The result is an increase in the melting point of the fat (increased hardness). Because hydrogen is added in the above reaction, and the fat is "hardened", the fat obtained by this treatment is different from the original nature, called "hydrogenated oil" or "hardened oil", and the process is also called "hydrogenation".
2. Hydrogenation process
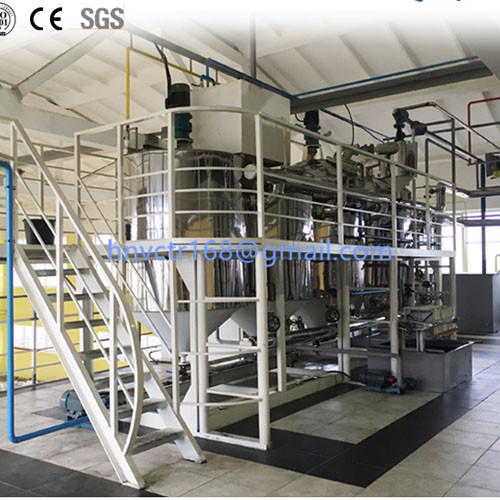
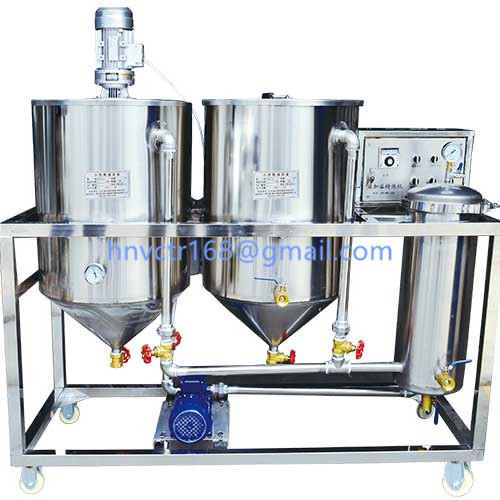
Raw oil → pretreatment (refining) → deoxygenation, dehydration → (catalyst →) hydrogenation → (hydrogen →) filtering → re-bleaching → deodorization → hydrogenated oil.
When heating vegetable oils containing a lot of unsaturated fatty acids, add metal catalysts (nickel series, copper-chromium series, etc.) to pass hydrogen gas, so that the double bonds in the unsaturated fatty acid molecules combine with hydrogen atoms to become fatty acids with a lower degree of unsaturation. The result is an increase in the melting point of the fat (increased hardness). Because hydrogen is added in the above reaction, and the fat is "hardened", the fat obtained by this treatment is different from the original nature, called "hydrogenated oil" or "hardened oil", and the process is also called "hydrogenation".
2. Hydrogenation process
Raw oil → pretreatment (refining) → deoxygenation, dehydration → (catalyst →) hydrogenation → (hydrogen →) filtering → re-bleaching → deodorization → hydrogenated oil.
Hot tags:Hydrogenated oil,oil hydrogenation,Hydrogenation process