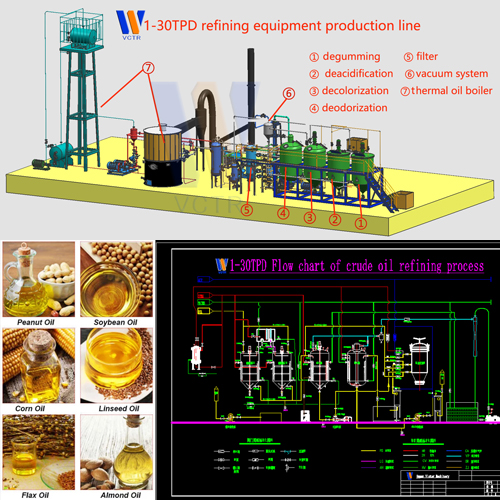
Oilseed and oil processing technology-Condensation and cooling of solvent vapor
1. Process flow
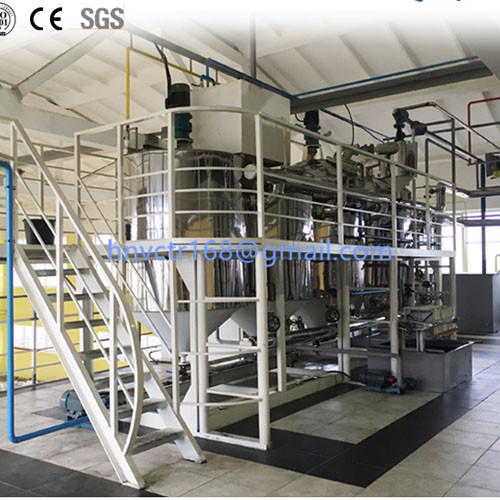
Since the solvent vapor from the first and second evaporators does not contain water, it flows directly into the circulating solvent tank after being cooled by the cold exchanger;The mixed vapor from the stripping column and desolventizer-toaster enters the condenser, and the condensed solvent and water mixture flows into the water separator for water separation. The separated solvent flows into the circulating solvent tank, and the water enters the water seal tank, and then drain into the sewer.
If the water discharged from the water separator contains solvent, it will enter the boiling tank, after the trace solvent in the water is evaporated, the condensate will enter the water separator through the condenser, and the waste water will enter the water seal tank.
2. Condensation and cooling of solvent vapor
The so-called condensation refers to the process in which gas emits heat and turns into liquid at a certain temperature. And cooling refers to the process in which the temperature of the hot fluid releases heat but does not change phase. A single solvent vapor releases its own latent heat of vaporization at a fixed condensation temperature and changes from a gaseous state to a liquid state.When the vapor has just been condensed, the cooling process of the condensate begins. Therefore, the two processes of condensation and cooling are carried out in the condenser. In fact, these two processes cannot be completely separated.
The two immiscible vapor mixtures—water vapor and solvent vapor—because their respective condensation points are different, so during the condensation process, the composition of the resulting condensate is different as the temperature drops. But in the condenser, they still undergo two processes of condensation and cooling.
At present, the commonly used condensers are pipe bundle condenser, spraying condenser and plate condenser.
3. Solvent and water separation
After condensing the mixed vapor from the stripping column or desolventizer-toaster, it contains more water. The solvent is not easily soluble in water and lighter than water to separate the solvent from water to recover the solvent. This kind of separation equipment is called a "solvent-water separator", and the water separation tank is more commonly used at present.
4. Recovery of solvent in waste water
The waste water discharged from the water separation tank shall be treated by a water seal tank. The water seal tank should be close to the solvent extraction workshop. The water seal tank is a three-chamber cement structure. Its protection height should not be less than 0.4 meters. The height of the enclosed water column should be 2.4 times greater than the protection height, and the capacity should not be less than 1.5 times the volume of the workshop water tank. , The inlet and outlet pipes of the water flow are all water closed.
Under normal circumstances, the waste water discharged from the water separator is treated by a water seal tank, but when there is a large amount of dregs in the water, a part of the waste water in an emulsified state should be sent to the waste-water boiling tank and heated to above 92°C with steam. but not exceeding 98°C, so that the solvent contained in it evaporates, and then recovered by the condenser.
Since the solvent vapor from the first and second evaporators does not contain water, it flows directly into the circulating solvent tank after being cooled by the cold exchanger;The mixed vapor from the stripping column and desolventizer-toaster enters the condenser, and the condensed solvent and water mixture flows into the water separator for water separation. The separated solvent flows into the circulating solvent tank, and the water enters the water seal tank, and then drain into the sewer.
If the water discharged from the water separator contains solvent, it will enter the boiling tank, after the trace solvent in the water is evaporated, the condensate will enter the water separator through the condenser, and the waste water will enter the water seal tank.
2. Condensation and cooling of solvent vapor
The so-called condensation refers to the process in which gas emits heat and turns into liquid at a certain temperature. And cooling refers to the process in which the temperature of the hot fluid releases heat but does not change phase. A single solvent vapor releases its own latent heat of vaporization at a fixed condensation temperature and changes from a gaseous state to a liquid state.When the vapor has just been condensed, the cooling process of the condensate begins. Therefore, the two processes of condensation and cooling are carried out in the condenser. In fact, these two processes cannot be completely separated.
The two immiscible vapor mixtures—water vapor and solvent vapor—because their respective condensation points are different, so during the condensation process, the composition of the resulting condensate is different as the temperature drops. But in the condenser, they still undergo two processes of condensation and cooling.
At present, the commonly used condensers are pipe bundle condenser, spraying condenser and plate condenser.
3. Solvent and water separation
After condensing the mixed vapor from the stripping column or desolventizer-toaster, it contains more water. The solvent is not easily soluble in water and lighter than water to separate the solvent from water to recover the solvent. This kind of separation equipment is called a "solvent-water separator", and the water separation tank is more commonly used at present.
4. Recovery of solvent in waste water
The waste water discharged from the water separation tank shall be treated by a water seal tank. The water seal tank should be close to the solvent extraction workshop. The water seal tank is a three-chamber cement structure. Its protection height should not be less than 0.4 meters. The height of the enclosed water column should be 2.4 times greater than the protection height, and the capacity should not be less than 1.5 times the volume of the workshop water tank. , The inlet and outlet pipes of the water flow are all water closed.
Under normal circumstances, the waste water discharged from the water separator is treated by a water seal tank, but when there is a large amount of dregs in the water, a part of the waste water in an emulsified state should be sent to the waste-water boiling tank and heated to above 92°C with steam. but not exceeding 98°C, so that the solvent contained in it evaporates, and then recovered by the condenser.