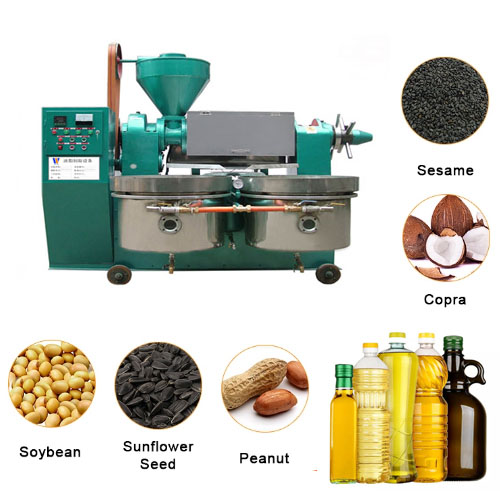
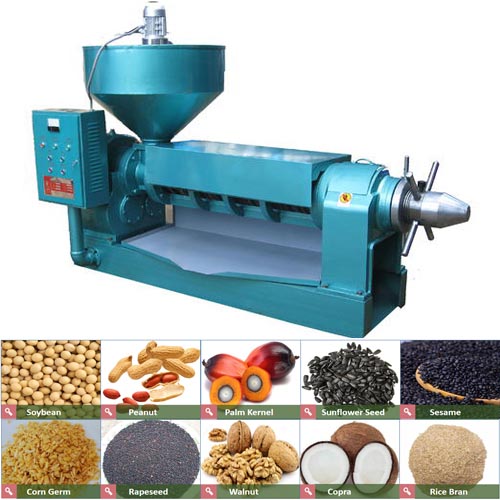
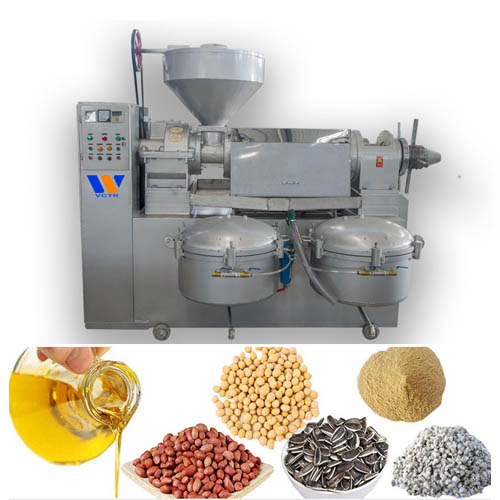
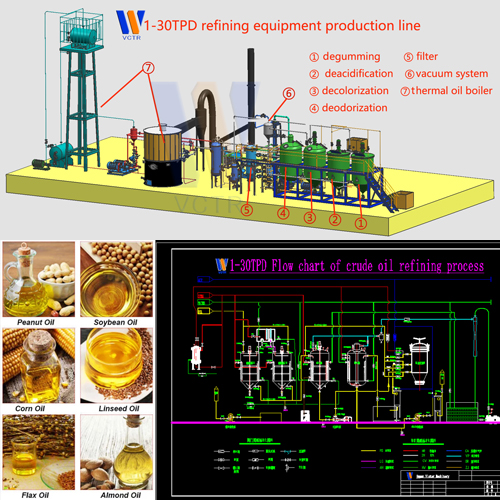
The influence of operation process on adsorption bleaching

Pure triglycerides are colorless when they are liquid, but in common vegetable oils, they show different colors because they contain different quantities and qualities of pigments. Most pigments are non-toxic, but they will affect the appearance of the oil. There are also by-products that are not conducive to the quality of oils and fats, including certain harmful substances that are not conducive to food safety and hygiene, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons caused by pollution, oxidative deterioration substances and so on. Therefore, the oils and fats must be bleached. The most widely used in industrial production is the adsorption bleaching method.
The adsorption bleaching of oils and fats is to use certain substances with strong selective adsorption of pigments to adsorb pigments or other impurities under certain conditions, and then remove the adsorbent through filtering equipment to achieve the purpose of oil bleaching. The factors affecting adsorption bleaching include the following key factors in the operation process:
Oil quality
The natural pigments of oils are relatively easy to remove, but the new pigments formed during the storage or oxidation of oils are difficult to remove. Degradation products such as protein and phospholipids (usually dark brown), iron soap produced by the interaction of free fatty acids and iron ions, etc., are difficult to remove due to the poor selectivity of the adsorbent. Therefore, it is very important to avoid oxidation of oil during storage and processing.
Operating temperature
The increase in temperature makes the movement of molecules more intense, and accelerates the diffusion speed of the outside/inside in the liquid phase around the adsorbent, thereby increasing the adsorption efficiency. But as the adsorption speeds up, the side reaction-the oxidation of oils and fats will also speed up, so there is an optimal temperature T.
The optimal temperature T depends on the type, characteristics and operating pressure of oils and fats adsorbent.
Operating pressure
In the process of adsorption bleaching of oils and fats, in addition to adsorption, there is also a side reaction-thermal oxidation. This side reaction will produce new pigments and affect the stability of the oil.
At present, the common bleaching reactions in various countries are negative pressure bleaching. During the negative pressure bleaching process, due to the low operating pressure, the amount of oxides introduced is small, and the thermal oxidation side reaction has little effect, thereby reducing the production of new pigments in oils.
Different types of oils and adsorbents have different bleaching effects under different pressure conditions. For example, adsorbents with high activity and oil with low saturation are suitable for bleaching under negative pressure, while adsorbents with low activity are suitable for bleaching under negative pressure. For example, natural bleaching soil and highly saturated fats are suitable for bleaching under normal pressure. Because of the low catalytic oxidation performance of adsorbents with low activity, the degree of adsorption and fading exceeds the generation of new pigments.
Reaction time
The length of the reaction time depends on the adsorption equilibrium, and it only needs to be stirred sufficiently, and the time to reach the adsorption equilibrium does not need to be too long. Although the degree of adsorption bleaching will deepen with the extension of the reaction time, excessive extension of the time will also cause the color to rise, the acid value to rise, and the fat to oxidize.
Fats adsorbed at high temperatures may also undergo fatty acid double bond conjugation, so the reaction time can be controlled at 20 minutes during the bleaching process.
Stirring intensity
Adsorption is carried out on the surface of the adsorbent, which is a heterogeneous reaction. Good mixing, uniform contact, establish adsorption equilibrium as soon as possible, so as to avoid local long-term contact causing oil oxidation. In the negative pressure bleaching, the stirring intensity should not produce splashing oil; in the normal pressure bleaching, the stirring intensity should not be too high to reduce the occurrence of oxidation reaction.
To sum up, we can find the reason for the deterioration of the bleaching effect in the process. We might as well start from the above five points and analyze the problem in combination with the actual situation. Only by analyzing the nature of the problem can the problem be solved.