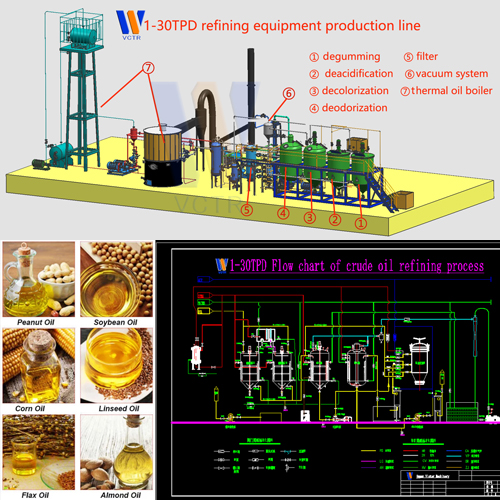
Three key points to measure healthy cooking oil

In our daily life, edible oil is a necessity, it makes our food more delicious. According to the survey, the average daily intake of edible oil per capita in urban residents in my country is as high as 44 grams, which greatly exceeds the 25 grams per capita intake recommended by the Chinese Nutrition Society. At present, the international medical community has confirmed that chronic diseases such as hyperlipidemia and coronary heart disease are closely related to excessive intake of oil. Therefore, while nutritionists are pushing the public to "eat less oil", they also call on the public to pay attention to their own nutrition and health, and to "eat good oil" to ensure normal nutritional intake. So, do you know how to choose cooking oil? Do you know what kind of oil is good for your health?
Edible oil is composed of glycerin and fatty acids, among which fatty acids are divided into saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids, and unsaturated fatty acids are further divided into monounsaturated fatty acids and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
1. Saturated fatty acid content
Saturated fatty acids are mainly found in animal oils and fats, such as lard and tallow, and a few are vegetable oils and fats, such as palm oil and coconut oil. It mainly provides energy for the human body. Insufficient intake will make the blood vessels of the human body brittle, prone to cerebral hemorrhage, anemia, and susceptible to diseases such as tuberculosis and neurological disorders. However, excessive intake is more harmful to human health. According to the definition of saturated fatty acid content in international nutrition standards: if saturated fatty acid content exceeds 12%, it will cause fat accumulation in the body, causing abnormal blood lipid levels, and induce serious cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as hyperlipidemia, hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc.
2. Oleic acid content
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid. The International Nutrition Society argues that the nutritional value of edible oil mainly depends on the content of oleic acid, and the nutritional value of higher oleic acid content is higher. Oleic acid is also known as "beauty acid". Long-term consumption can moisturize the skin, delay the body's aging, improve memory, and have a significant improvement effect on high blood pressure, hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 2004 NIAN issued an announcement on November 1st: The average daily intake of 23 grams of monounsaturated fatty acids per capita can greatly reduce the incidence of coronary heart disease.
3. The proportion of non-fatty acids
Linoleic acid (ω-6) and linolenic acid (ω-3) are both polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are essential fatty acids for the human body, but the human body cannot synthesize by itself and must be taken from outside. If the intake of linoleic acid and linolenic acid is not balanced, it will easily lead to a variety of diseases; if the intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids is excessive, harmful oxides and peroxides in the body will increase, which will cause a variety of chronic hazards. Only proper intake and adherence to the correct ratio can effectively localize the occurrence of a series of diseases. Therefore, the intake ratio of polyunsaturated fatty acids for different age groups recommended by the Chinese Nutrition Society is:
Age (ω-3): (ω-6)
0-1 years old: 1:4;
2-60 years old: 1:4-1:6;
Over 60 years old: 1:4.
Edible oil is composed of glycerin and fatty acids, among which fatty acids are divided into saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids, and unsaturated fatty acids are further divided into monounsaturated fatty acids and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
1. Saturated fatty acid content
Saturated fatty acids are mainly found in animal oils and fats, such as lard and tallow, and a few are vegetable oils and fats, such as palm oil and coconut oil. It mainly provides energy for the human body. Insufficient intake will make the blood vessels of the human body brittle, prone to cerebral hemorrhage, anemia, and susceptible to diseases such as tuberculosis and neurological disorders. However, excessive intake is more harmful to human health. According to the definition of saturated fatty acid content in international nutrition standards: if saturated fatty acid content exceeds 12%, it will cause fat accumulation in the body, causing abnormal blood lipid levels, and induce serious cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases such as hyperlipidemia, hypertension, atherosclerosis, etc.
2. Oleic acid content
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid. The International Nutrition Society argues that the nutritional value of edible oil mainly depends on the content of oleic acid, and the nutritional value of higher oleic acid content is higher. Oleic acid is also known as "beauty acid". Long-term consumption can moisturize the skin, delay the body's aging, improve memory, and have a significant improvement effect on high blood pressure, hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) 2004 NIAN issued an announcement on November 1st: The average daily intake of 23 grams of monounsaturated fatty acids per capita can greatly reduce the incidence of coronary heart disease.
3. The proportion of non-fatty acids
Linoleic acid (ω-6) and linolenic acid (ω-3) are both polyunsaturated fatty acids, which are essential fatty acids for the human body, but the human body cannot synthesize by itself and must be taken from outside. If the intake of linoleic acid and linolenic acid is not balanced, it will easily lead to a variety of diseases; if the intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids is excessive, harmful oxides and peroxides in the body will increase, which will cause a variety of chronic hazards. Only proper intake and adherence to the correct ratio can effectively localize the occurrence of a series of diseases. Therefore, the intake ratio of polyunsaturated fatty acids for different age groups recommended by the Chinese Nutrition Society is:
Age (ω-3): (ω-6)
0-1 years old: 1:4;
2-60 years old: 1:4-1:6;
Over 60 years old: 1:4.